可视化 1.0版本
前端的数据可视化越来越重要,炫酷大屏的需求越来越多,您是否经常为屏幕不能自适应而烦恼?如何高度还原设计稿?如何在多种终端都呈现完美效果?
当屏幕宽高比例小于设计稿时,按设计稿比例沿水平方向铺满屏幕。当屏幕宽高比大于设计稿时,按设计稿比例沿垂直方向铺满屏幕。用等比缩放的方式,不论屏幕多大,分辨率是什么,都能呈现完美效果。
最终想要实现的效果类似此种:https://sugar.aipage.com/dataPortalShare/SugarBI?menu=m_l4dxdax22rvvs
实现思路
根据 UI 提供的设计稿,定义页面长宽基准值(如:w-1920 * h-969)基于此长宽比,进行等比例放大缩小,垂直居中显示。定义了页面基准值后,这时候我需要用到页面视口长宽,这里我用的是 document.documentElement.clientWidth 和 document.documentElement.clientHeight 来获取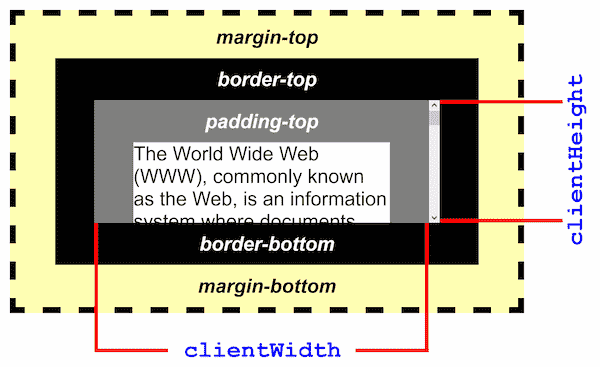
然后基于页面视口的长宽和 UI 设计稿的基准长宽做对比,就可以算出页面缩放了多少,视口的长宽去掉缩放后的基准长宽剩下的值就是页面空白的区域(空白区域填充默认底色),然后去除一半值后,就可以实现居中的效果了。
基于 transform 的等比例缩放自适应方案
mdn transform 是什么,CSS transform 属性允许你旋转,缩放,倾斜或平移给定元素,这是通过修改 CSS 视觉格式化模型的坐标空间来实现的。
效果图

具体实现
父组件
<template>
<div class="app-content">
<ScreenAdapter>
这里是大屏的具体页面
</ScreenAdapter>
</div>
</template>
<style lang="scss" scoped>
// 用来填充大屏超出的底色部分
.app-content {
background-color: #1c1d20;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
</style>
子组件(ScreenAdapter)
<template>
<div class="screen-adapter" :style="style">
// slot 会把大屏的页面传递过来,这样的话 只需要关注自己的页面
// 等比例伸缩的逻辑就不用管 交给 ScreenAdapter 就可以了
<slot />
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { debounce } from "lodash";
export default {
props: {
width: {
type: String,
default: "1920",
},
height: {
type: String,
default: "969",
},
},
data() {
return {
style: {
width: this.width + "px",
height: this.height + "px",
transform: "scale(1)",
margin: "0"
},
// 判断缩放的是 X轴 还是 Y轴 就可以将空出来的区域通过 margin 来区分是水平还是垂直方向上的居中
isXaxis: true,
};
},
mounted() {
this.setScale();
window.onresize = debounce(this.setScale, 300);
},
methods: {
// 获取放大缩小比例
getScale() {
const w = document.documentElement.clientWidth / this.width;
const h = document.documentElement.clientHeight / this.height;
this.isXaxis = w < h ? false : true;
return w < h ? w : h;
},
// 设置比例
setScale() {
this.style.transform = "scale(" + this.getScale() + ")";
const widthScale = this.width * this.getScale();
const heightScale = this.height * this.getScale();
const xxWidth = (document.documentElement.clientWidth - widthScale) / 2;
const yyHeight =
(document.documentElement.clientHeight - heightScale) / 2
const xAxixMargin = this.isXaxis ? xxWidth : 0;
const yAxixMargin = !this.isXaxis ? yyHeight : 0;
this.style.marginLeft = xAxixMargin + 'px';
this.style.marginRight = xAxixMargin + 'px';
this.style.marginTop = yAxixMargin + 'px';
this.style.marginBottom = yAxixMargin + 'px';
},
},
};
</script>
<style lang="scss" scoped>
.screen-adapter {
transform-origin: 0 0;
position: absolute;
left: 0;
top: 0;
transition: 0.3s;
background: #1c1d20;
}
</style>
可视化 2.0版本
在1.0的基础上进行了动态缩放组件的改进,通过对当前屏幕伸缩的宽高、以及设计稿的宽高进行独立的计算,得出各自的伸缩比,而不是通过1.0版本中视口的宽高对比设计稿的宽高进行对比得到对应的伸缩比。
升级的2.0版本除了计算方式上做了调整,另外语法上也升级了对vue3的兼容(上面1.0版本是vue2的语法),适配vue3项目的语法。
<template>
<div class="screen-adapter" :style="style">
<slot />
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, onMounted } from "vue";
import { debounce } from "lodash";
// 初始设计稿宽高
const designWidth = "1920";
const designHeight = "969";
const style = ref({
width: designWidth + "px",
height: designHeight + "px",
transform: "scale(1)",
margin: "0",
});
// 获取缩放比
const getScale = () => {
// 获取对应的宽高比
const screenRatio =
document.documentElement.clientWidth /
document.documentElement.clientHeight;
const designRatio = designWidth / designHeight;
return {
// x轴是否缩放满屏,此时y方向需要居中
xFit: screenRatio < designRatio,
// 取小的缩放比
scale:
screenRatio < designRatio
? document.documentElement.clientWidth / designWidth
: document.documentElement.clientHeight / designHeight,
};
};
// 大屏自适应函数
const setScale = () => {
const { xFit, scale } = getScale();
const adjustedWidth = designWidth * scale;
const adjustedHeight = designHeight * scale;
// 没有铺满的一侧 进行居中
const marginWidth = document.documentElement.clientWidth - adjustedWidth;
const marginHeight = document.documentElement.clientHeight - adjustedHeight;
const xMargin = xFit ? 0 : marginWidth / 2; // 左右居中
const yMargin = xFit ? marginHeight / 2 : 0; // 上下居中
style.value.transform = `scale(${scale})`;
style.value.marginLeft = xMargin + "px";
style.value.marginRight = xMargin + "px";
style.value.marginTop = yMargin + "px";
style.value.marginBottom = yMargin + "px";
};
onMounted(() => {
setScale();
window.onresize = debounce(setScale, 300);
});
</script>
<style lang="scss" scoped>
.screen-adapter {
transform-origin: 0 0;
position: absolute;
left: 0;
top: 0;
transition: 0.3s;
background: #00142d;
}
</style>
具体使用的话不变,引入组件,将内部包裹的页面通过slot插槽的方式进行处理即可。
小结
基于transform缩放的方案,优点是按设计稿设置元素大小,无需转换长度单位。页面会根据页面设置的基准值和视口的长宽比做等比例的缩放且居中,以此达到适配大屏展示的效果。